Advanced git
Block 1.1: Reviewing git Basics
Jan Simson
Background: https://unsplash.com/photos/842ofHC6MaI
The Classic Git Flow
The 3 Levels of Changes in git
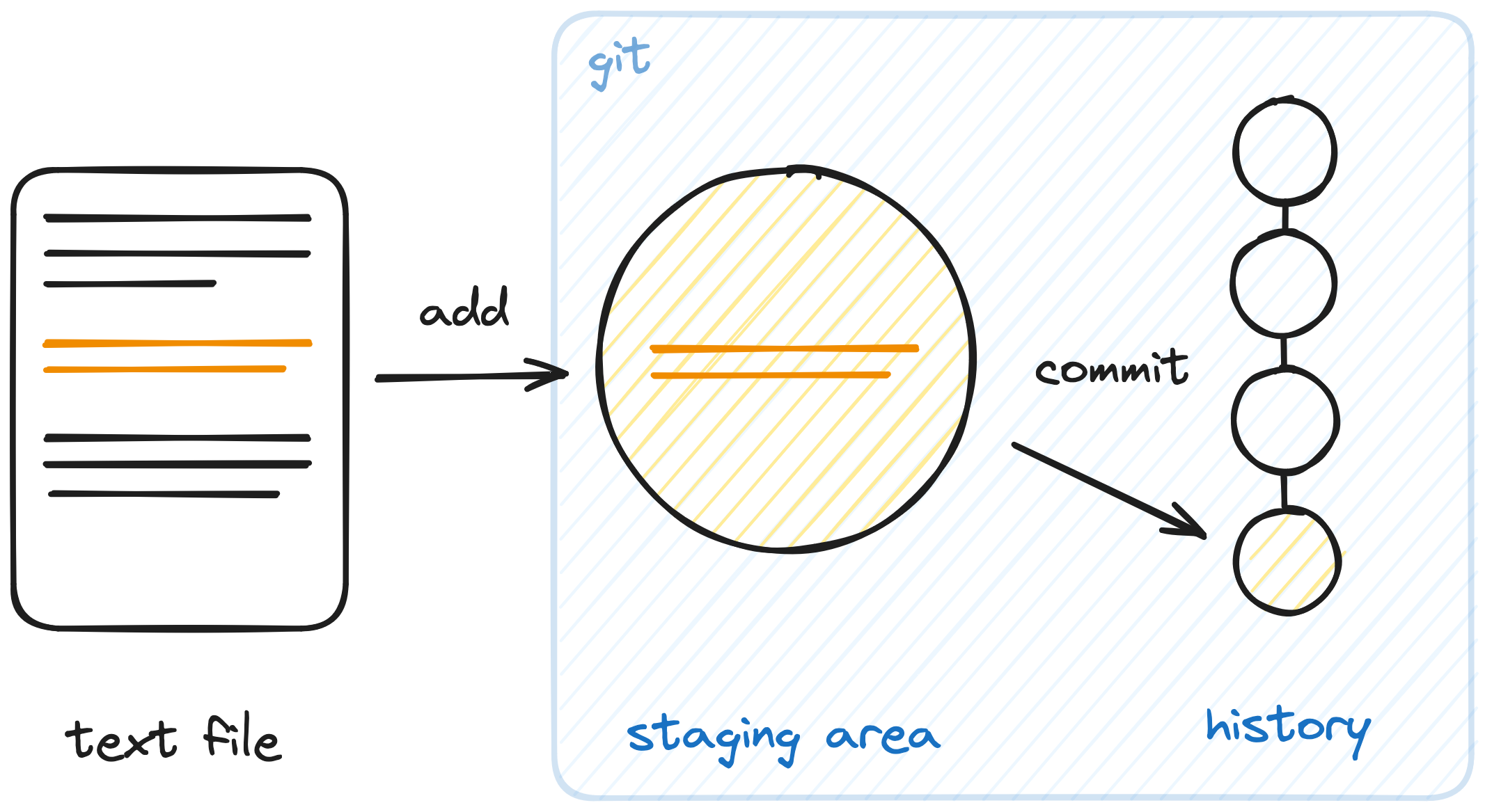
Changes can be either unstaged, staged or commited.
- When we first make a change it is unstaged
- Once we
addthe change to the staging area it is staged - We can then
commitall staged changes
The 3 Levels of Changes in git

Changes can be either unstaged, staged or commited.
- We can
restorethe commited version (and remove any unstaged changes)
A small addendum: git add -i
You can also interactively add changes with -i.
There’s also an extension available.
Practical: Cookbook (1)
- Create a new directory called
git-example - Initialize a git repository in the new directory
- Create a new file
cookbook.mdin yourgit-exampledirectory - Search for your favorite recipe online and copy the title into the file
- Tip: Use english language recipes
- Commit the changes
- Add the ingredients into the file and commit them, too
Practical: Cookbook (2)
- Add the cooking steps into the file and commit them
- Delete the
cookbook.mdand restore it - Explore the repo status & history
- Add a second recipe step by step
Expanding on .gitignore
- Old news: You can ignore files by adding them to
.gitignore📰 - Maybe new: You can reverse ignored files with a
!- e.g.
dir/**and!dir/.gitkeep
- e.g.
- Ignoring a directory:
dir/vs.dir/**- Q: What will happen with
dir/and!dir/.gitkeep?
- Q: What will happen with
- ❗️ With
dir/, the whole directory is ignored and git will not scan it at all
Empty directories: .gitignore > .gitkeep 📂
- git only tracks files, not directories
- If we want git to create a directory, but ignore all files it needs to track a file in there
- Common convention: Ignore all files except an empty
.gitkeep - Better: Create a
.gitignorefile in the directory with*and!.gitignore
https://adamj.eu/tech/2023/09/18/git-dont-create-gitkeep/
End of Section 🎉
Any Questions?